The way content is ranked online has changed. Content visibility and ranking go beyond just keyword integration. It is about creating content that appeals to search engine algorithms while at the same time resonating with human readers.
SEO-friendly content acts as a catalyst for online visibility, audience engagement and conversion rates. However, beneath these well-optimized content pieces lie critical issues that must be acknowledged and addressed.
Identifying and solving these SEO content issues is essential to avoid low web performance and rankings. Your content should align with the needs of your audience, be of high quality and meet technical requisites for search engine recognition.
You don’t need just to recognize SEO content issues; you must also develop strategies to rectify them. Read on to learn how to identify and solve your potential issues.
What are SEO content issues?
Content issues are problems that may arise in a website’s content and can negatively affect search engine rankings, user engagement, visibility and your overall website performance. These issues on the web pages revolve around content relevance, quality and optimization.
The role of content in determining rankings
Search engines act as gatekeepers and use content as a crucial ranking factor. Therefore, it’s essential to understand how they evaluate content quality, relevance and user value to overcome the common content issues.
According to Brian Njogu, the founder of Smart Profits Hub:
“Search engines love quality content because users love quality content. Creating content that genuinely addresses user intent and offers valuable insights improves SEO and creates a positive and lasting impression on your audience.”
Let’s look at some elements search engines look at when ranking content in a bit more depth.
Content relevance
You should aim to write content that aligns with users’ queries and more specifically their intent. Addressing these queries directly elevates the relevance of your content.
For example, if a user launches the search, “ride a bike,” they are likely looking for step-by-step instructions on how to learn or how to teach someone to ride a bike. They aren’t necessarily looking to for the best bike to ride or to immediately make a purchase, so the content you write should address that specific need.
Content quality
In 2011, Google released a Panda algorithm update, helping people find high-quality content in the SERPs. This update improved rankings for high-quality websites. On the other hand, websites with poor quality and thin content experienced a severe decline in rankings. Search engines prioritize high-quality content that is well-researched and provides its readers some value.
Keyword research
Keywords communicate to search engines what your content is about. You should use keywords strategically, in titles, headings, and meta descriptions, to make your content accessible.
Content freshness
Search engines also give preference to fresh and valuable content. Therefore, you need to keep your content up-to-date to ensure it’s relevancy and that it aligns with industry changes. Fresh content on your website will help you become credible and build trust.
Engagement metrics
Analyzing your user engagement metrics will help you know how your content is performing and give you ideas on how to adjust your strategies accordingly. When users spend more time on your content, it means they find it engaging and valuable.
Search engines reward websites with good engagement on their content since they aim to provide users with relevant and valuable content for their queries.
Comprehensiveness
Writing long-form content covers topics in depth and gives you a higher chance of ranking than short-form content because it has a higher probability of fully addressing a user query.
Multimedia elements
Using multimedia elements like images, infographics, videos and other media helps improve user experience by facilitating comprehension and creating a visually appealing and immersive environment. These elements not only capture attention but also make content more accessible, enjoyable, and memorable for users.
Readability and content structure
Well-structured and readable content will enhance user satisfaction. Content should be broken up with headings and bullet points to enhance the experience.
Original content
Unique content stands out because search engines, like Google and Bing, value original content that aims to provide new information and relevant content.
Links and structured data
Quality backlinks on your website can positively contribute to content credibility. Internal linking helps distribute page authority and guides your users into finding relevant and related content.
Content accessibility
It’s essential to ensure your content is accessible to search engines. If your content is difficult to access due to paywalls or aggressive pop-ups, it can negatively affect your SEO performance. Additionally, accessibility refers to making your content accessible and usable to different people with a variety of disabilities.
[Case Study] How Unilever’s recipe platform puts SEO first
Common content-related issues and solutions
Now that we have identified how important content really is for your SEO, let’s look at some content issues you might encounter and how you should go about fixing them:
Duplicate Content
Duplicate content is an SEO issue that refers to content which appears in more than one place, either on the same website or across different websites.
So, why does duplicate content matter in SEO?
- Search engines face challenges deciding which version of your duplicate content to include or exclude from their indices.
- Determining where to direct link metrics (trust, authority, anchor text) becomes ambiguous, impacting ranking decisions.
- Search engines struggle to identify which version(s) should rank for specific search queries.
- Duplicate content can lead to ranking and traffic losses due to search engines choosing one version over others.
- The visibility of each duplicate is diluted, impacting the overall search experience for users.
- Link equity is dispersed among duplicates, affecting the search visibility of the original content.
Duplicate content can happen for a number of reasons including:
- HTTP vs. HTTPS or WWW vs. non-WWW: Having separate website versions with the same content may lead to duplicate issues.
- Copied content: Republished blog posts or product information pages can result in duplicate content.
According to Silvia Gituto, Senior Content Writer and Strategist at Witty Content Writers:
“Solving duplicate content demands more than technical fixes. It requires strategic analysis, thoughtful canonicalization, and a commitment to producing unique, valuable content. This not only improves search rankings but establishes authority and consistency for users.”
Identify duplicate content
To identify if and where any duplicate content can be found on your site, you could use a tool like Oncrawl to explore your website. A crawl report will identify any duplicate content and from there you can decide the best way to address the issues.
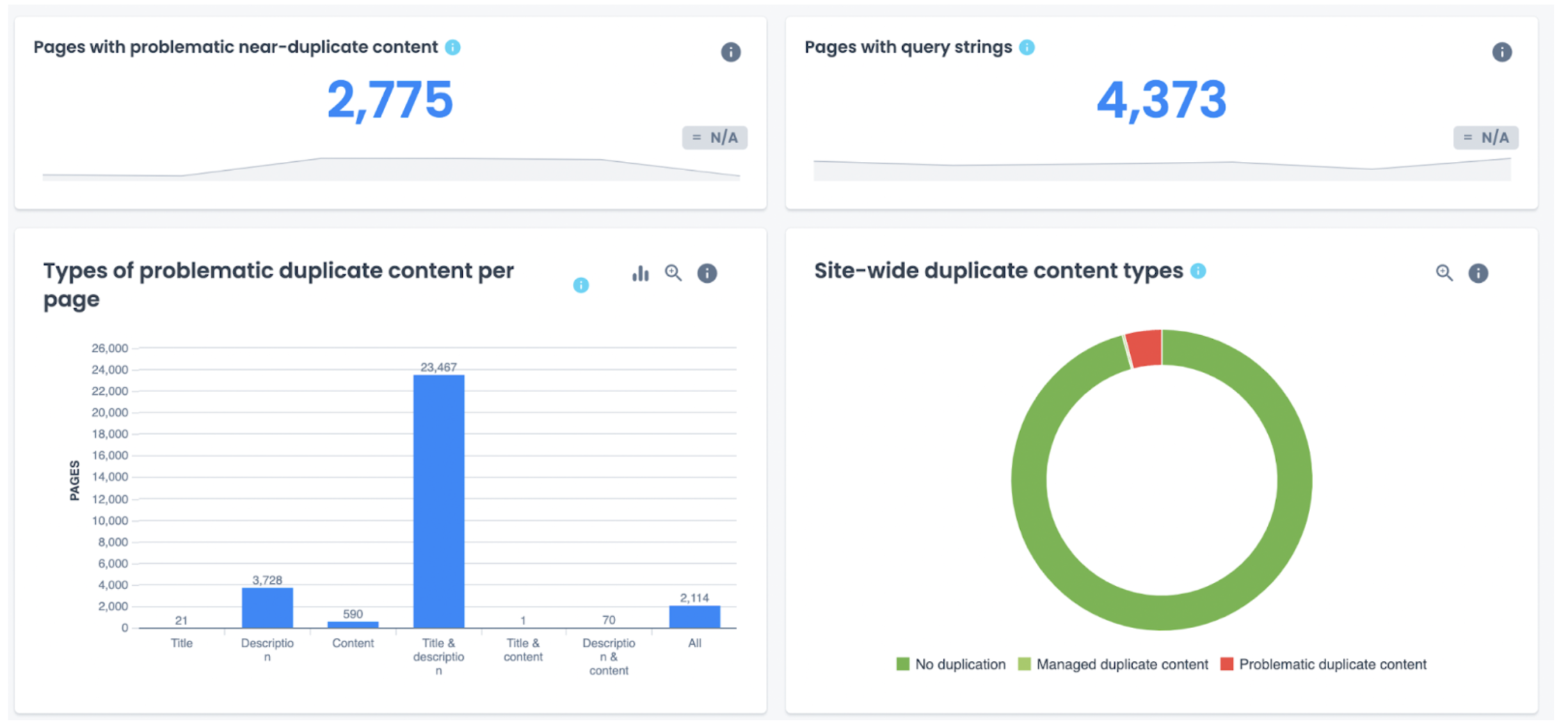
Conversely, if you’re doing your due diligence before publishing content on your site and want to make sure it doesn’t already exist elsewhere, you could turn to plagiarism checker tools like Copyscape or Grammarly. These tools help identify cases of duplicate content by comparing your content with an index of content available on the internet.
Additionally, you can also use Google Search Console to gain insights into potential duplicate content issues. GSC will help you check duplicate content by providing insights into how Google crawls and indexes your website, making it easier to pinpoint duplicate pages.
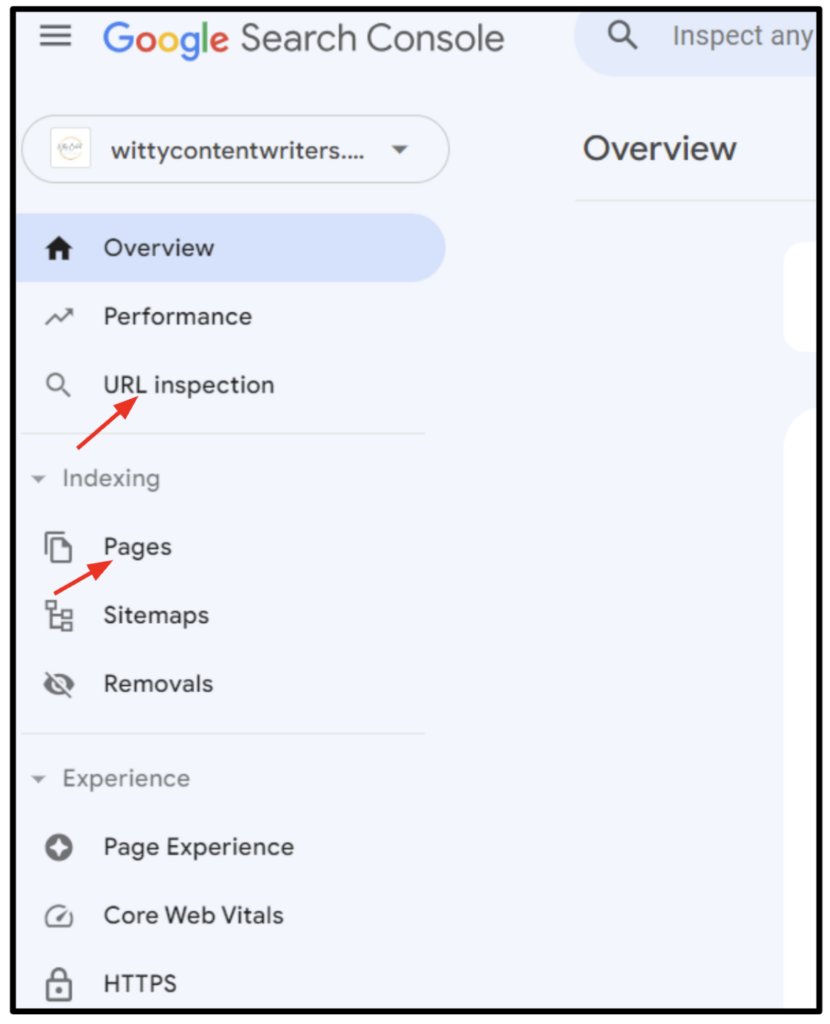
By navigating to the “Pages” and “URL Inspection” sections, you can verify whether duplicate URLs are being indexed. More specifically, you can see the:
- Presence of both HTTP and HTTPS versions of the same URL.
- Coexistence of www and non-www versions of the same URL.
- URLs with or without trailing slashes “/”.
- URLs with or without query parameters.
Fix duplicate content
Some steps you can take to resolve the problem of duplicate content include using a 301 redirect to permanently redirect duplicate pages to the original for optimal ranking and relevance.
You could also specify your preferred version using Rel=canonical tags to signal search engines the URL you want to be treated as the original version.
Additionally, you could consider using the “noindex” tag to exclude pages you don’t want to appear on the search engine result pages.
Keep in mind that you should also be aware when syndicating content, make sure the syndicating website links back to the original content accurately.
Thin or low-quality content
Thin content is a significant issue that refers to having content on a website lacking valuable information; it has little or no value to the user. Content is referred to as thin if:
- It lacks helpfulness or is plagiarized from other sources.
- It is full of typos and grammatical errors.
- It is well-written but lacks educational value.
- Content that is automatically generated and has not been reviewed by a human.
- Insufficiently short to convey necessary information.
- The content lacks depth, structure or overall quality.
- It contains redundancy or duplication of content.
Identify thin or low-quality content
A couple of quick ways to identify thin content is either by checking the depth of potential problem pages or looking at bounce rates.
Content is generally considered thin if your content lacks meaningful information, doesn’t add value, or is excessively brief. Such pages are often found buried deep on your site.
Furthermore, by analyzing bounce rates using Google Analytics, you’ll see if users quickly leave a page without engaging with the content, it shows that it did not meet their expectations or needs.
For a more thorough analysis, don’t hesitate to use crawlers to explore your site to identify thin content.
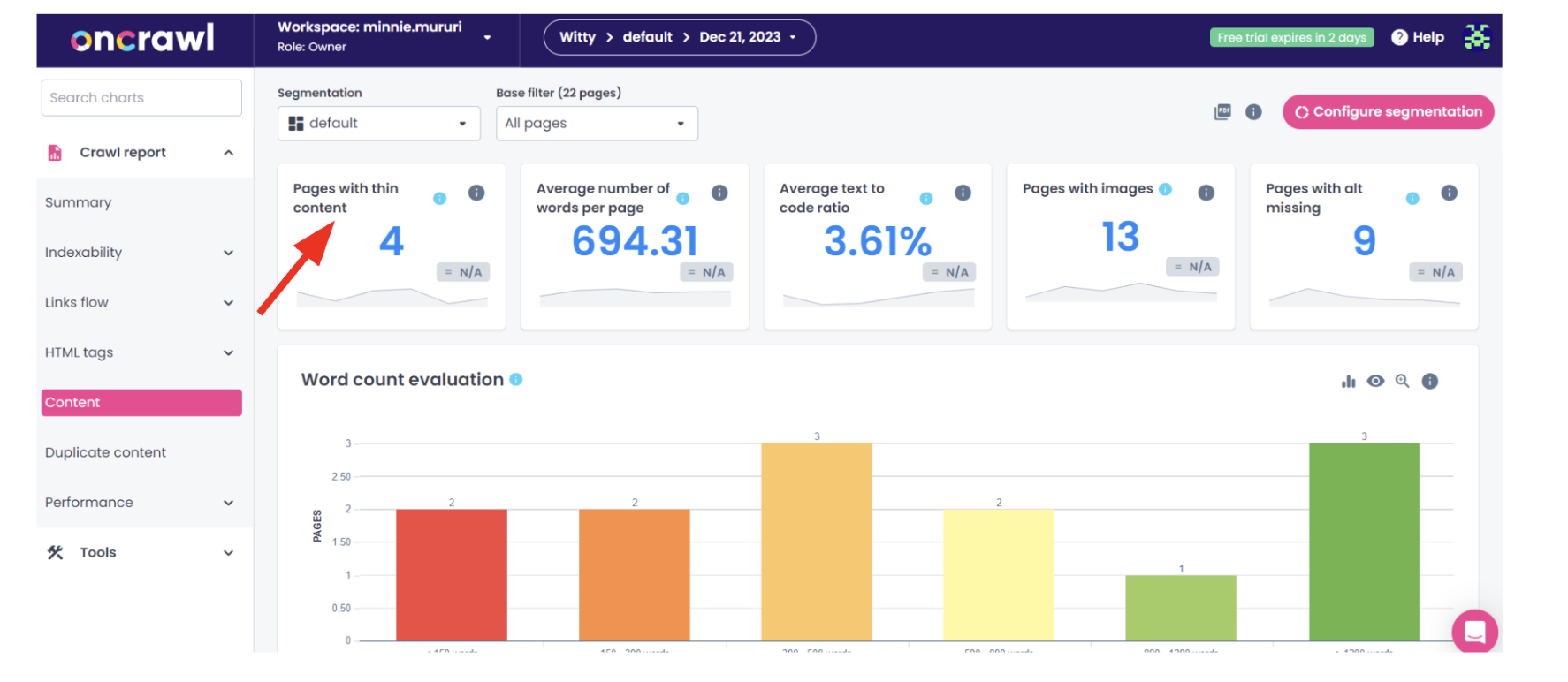
Source: Oncrawl
Once you’ve identified the thin content, assess whether the content directly addresses the user’s query. If it doesn’t, that is a pretty good indication that it will be considered low quality by search engines and you should take steps to rectify the problem.
Fix thin or low-quality content
There are several ways you can fix thin content on your website:
- Rewrite thin content to provide more value to visitors. Make sure your content is original, well-written, and informative.
- Remove thin content that does not provide value to visitors or is outdated.
- Consolidate thin content into a comprehensive page that provides more value to visitors.
- Include multimedia elements in your content, such as images, videos, or infographics, to enhance the value of the content.
Missing or irrelevant metadata
Missing or irrelevant metadata refers to the absence of inaccurate metadata, such as meta descriptions, meta titles and meta tags.
These elements are essential for providing context to your web content. Missing or having irrelevant metadata can impact how search engines interpret and display your content.
The occurrence becomes an issue when the metadata information is not provided at all. For example, a page may be missing title tags, meta description, and alt text for the images. On the other hand, irrelevant metadata is related to when metadata provided doesn’t accurately represent the published content.
Identify missing or irrelevant metadata
You can identify missing or irrelevant metadata in your content by auditing your website using tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush.
On the other hand, you could audit your website manually. Review your web pages individually to ensure they have relevant and accurate metadata, including titles, descriptions and tags. Bear in mind that this option could potentially be very time consuming.
Fix missing or irrelevant metadata
Multiple options for fixing metadata are available:
- Ensure every page has a unique and descriptive title tag, a relevant meta description, and appropriate attributes for images. This helps search engines understand the content.
- Review your existing metadata and make improvements where necessary. Ensure your titles and descriptions accurately reflect your content.
- Make sure your metadata matches with the content on the page. Avoid misleading or clickbait metadata that may result in a mismatch between user expectations and the published content.
- Schedule regular audits to check for new metadata issues and ensure that metadata is consistently added and optimized.
- Implement schema markup to help search engines understand the context of your content and can enhance rich snippets in search results.
- Test how your content appears in search results using plugins like Yoast and RankMath and monitor user engagement using Google Analytics. Adjust metadata based on performance and user feedback.
Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing is a black hat SEO technique where a page is loaded with excessive keywords to manipulate a website’s rankings in the search engine results. Google and other search engines have caught on and implemented measures to penalize websites that employ the technique.
According to Heba Said, international SEO Consultant at hebasaid.co:
“Keyword stuffing is a common SEO hiccup, especially in the MENA region. The real magic in SEO is speaking the language of humans, not just algorithms. Google has been singing that tune for years, and it actually works! Focus on crafting SEO content that serves users.”
Identify keyword stuffing
You can use several techniques to identify if you have stuffed keywords on your pages and the first one starts with simply reading through the content aloud. If you feel it sounds awkward, forced, or unnatural due to overused keywords, it’s likely stuffed. You should always prioritize natural and readable content.
Next, do a quick visual check to see if you have sections within your content where the same keywords are repeated excessively. Again, making sure your text reads as naturally as possible should always be a priority.
Assess whether the keywords used are genuinely relevant to the content. It could be a sign of stuffing if they seem forced or unrelated.
Also, think about checking whether your meta tags (title tags and meta descriptions) are loaded with keywords but lack meaningful information and whether the use of keywords disrupts your content’s flow and coherence. If they do, it’s another sign of keyword stuffing.
Finally, you can always turn to tools like WPBeginner Keyword Density Checker to check the keyword density of your content.
Fix keyword stuffing
If you have a keyword stuffing issue on your content, it’s essential to address it to improve your website’s performance and user experience. By regularly monitoring and promptly addressing keyword stuffing issues, you’ll be able to maintain an authoritative website. Some ways to address keyword stuffing include:
- Taking out any keywords that are not relevant or necessary to the content, and make sure your content reads naturally.
- Focusing on creating valuable and engaging content that addresses users’ needs and interests.
- Using secondary keywords, keywords synonyms, and long-tail keywords to improve search engine visibility.
A lack of fresh content
A lack of fresh content is usually the result of a website failing to update its content or add new relevant information regularly. Such content can negatively affect user engagement among other things.
Any site can fall victim to out-of-date content, so it’s important to assess your pages regularly. Here, GSC can be useful once again as it can help to single out your website’s underperforming or outdated content. After identifying underperforming pages, try to figure out the why. It could be due to the fact that the content is no longer up-to-date.
You can also use Google Analytics to check how users are engaging with your content. A decrease in user engagement, such as low time spent on a page, high bounce rate, or low click-through rate, is a sign that you should check whether your content is still relevant.
Refresh old content
If you have fresh content issues on your website, focus on fixing it by adding new information, updating stats, rewriting sections, or incorporating recent developments related to the topic. Come up with a schedule for checking and updating your content regularly to ensure it remains fresh and relevant. Be sure to monitor your website’s performance and make improvements as needed.
Beyond updating your old content, don’t neglect to develop new, relevant content that addresses current trends or industry changes. Focus on creating high-quality content that covers topics of interest for your target audience and that provides value by acknowledging their needs.
Poorly structured content
Poorly structured content is another issue that impacts how well audiences understand your content. Well-structured, readable content can better achieve your intended goals of informing, persuading, or engaging your audience.
Identify and fix poorly structured content
Any writer will tell you that the first step to fix any structure problems is reading through it. Check your contant’s readability and make sure it’s written using short sentences with simple language. You can use online tools like Hemingway Editor to analyze your content’s readability. Such tools will also give you suggestions on how to amend your content’s structure.
It’s also important to ensure your content is well structured with your header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc) that give a clear hierarchy to your content. The main topic should be an H1 tag followed by H2s as subtopics. When using headers, read through your content and make sure it has a logical flow and sequence, guiding the reader from one point to the next seamlessly.

Image source: Scope
Some other tips to consider when assessing the structure of your content:
- Use short paragraphs and sentences. Breaking down long paragraphs makes content easier to digest and appears less daunting at first glance.
- Employ consistent formatting throughout your content. Always use the same font, text size, and spacing throughout your content for a professional appearance.
- The use of numbers and bullets in your content makes it easier to scan and helps with organization and clarity.
- Add relevant images, videos, and infographics to your content to break up the text and provide visual context. This will help you improve engagement and understanding.
Broken Links
Having broken links on your website is an issue that not only affects how search engines regard your site, but also has a negative impact on your website’s credibility.
Imagine using a bridge to help you reach your destination only to realize it’s broken and thus preventing you from getting to your destination. Broken links have the same effect; they prevent users from accessing certain content on your site and consequently leads to frustration and a higher bounce rate.
If some users don’t bounce, running into enough broken links can ultimately cause them to lose trust in your website and regard it as unprofessional and unreliable. Let’s not forget that they can also result in missed opportunities for conversion that could have contributed to your business goals. All in all, they should be avoided whenever possible.
Identify broken links
Broken links occur over time and are caused by changes in your website structure, content updates or even external website changes. It’s essential to monitor your website’s links regularly to ensure your links are functional.
During a crawl of your site, Oncrawl will explore your website and identify broken links in a dedicated status codes report.
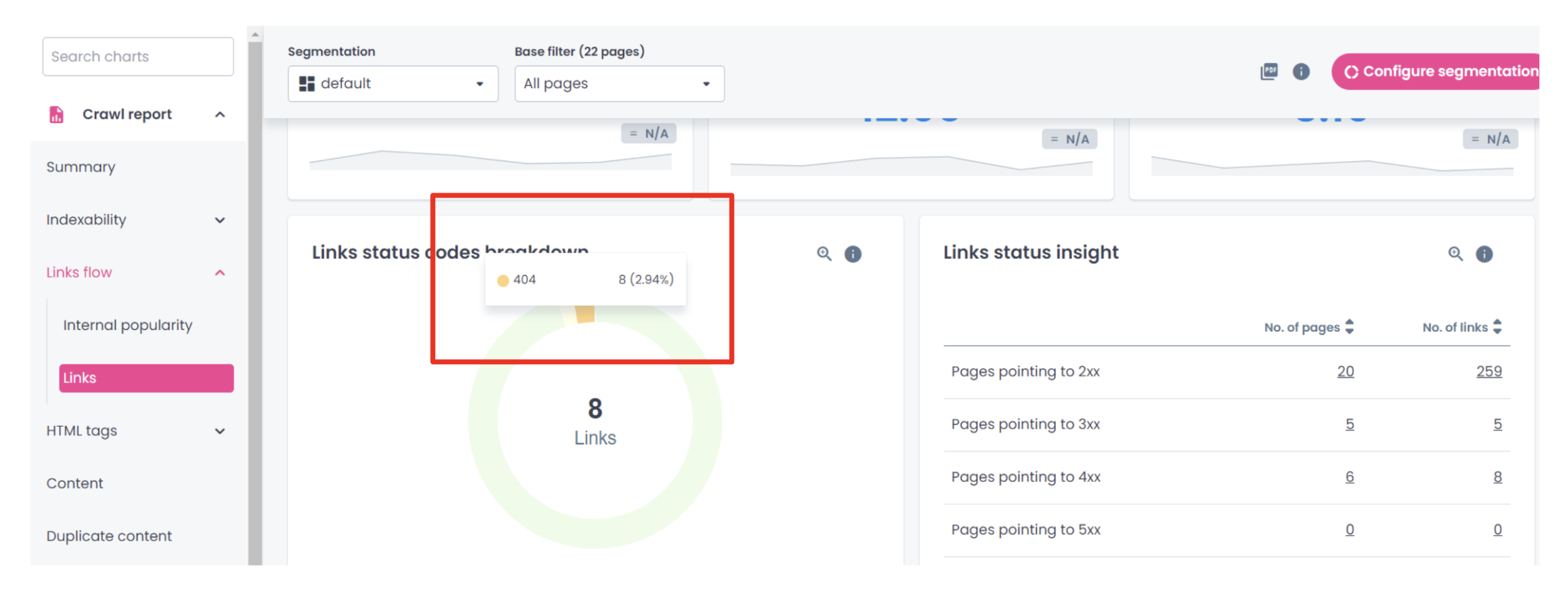
You can also use GSC’s Page Indexing report to see why certain pages aren’t being indexed. One of the main reasons, as you can see below, is that the pages are producing a 404 error, meaning they can’t be found.
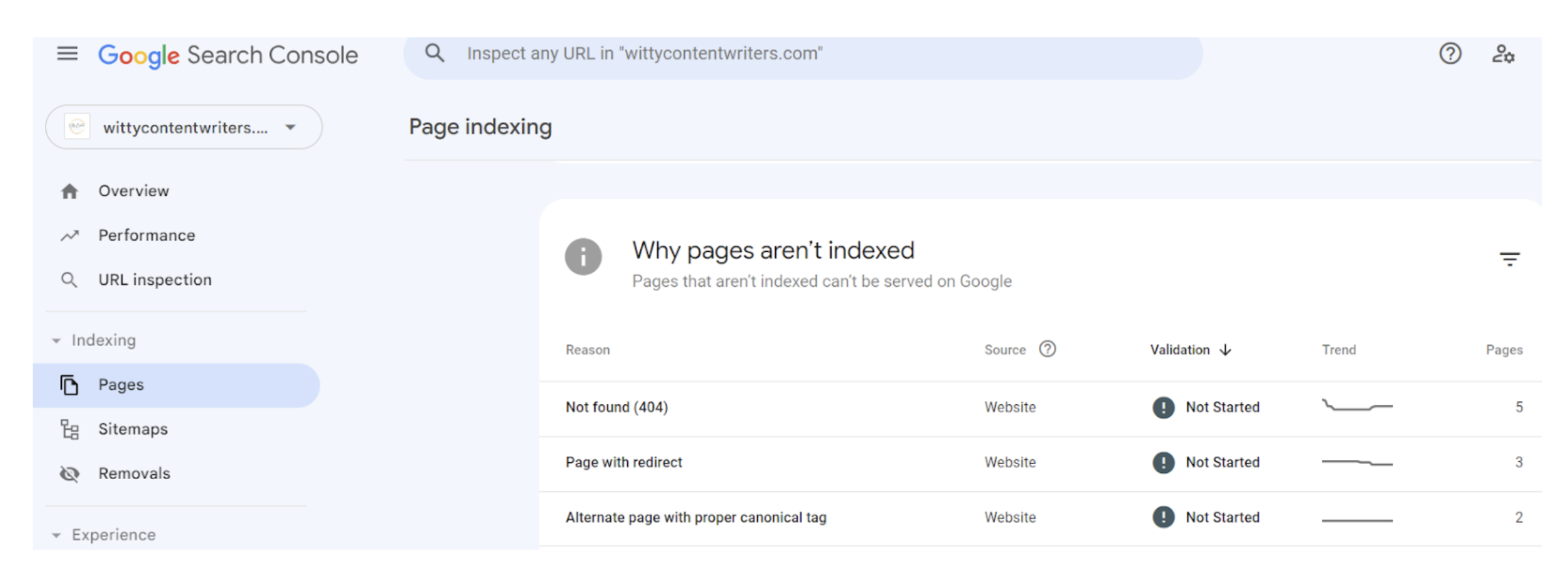
Although less popular, another option includes checking broken links manually. While checking broken links manually can be tiresome, the process could prove helpful in identifying links that automated tools might have missed.
When employing this process, click on each link and verify if it redirects to the right destination or returns an error. Alternatively, you can use browser extensions like BrokenLinkChecker to facilitate the manual process.
Fix broken links
When you’ve identified broken links, do your best to fix them as quickly as possible by:
- Updating your links accordingly if they have been moved or changed. Make sure that all your internal and external links are pointing to the correct URLs.
- Using 301 redirects to guide users to the new URL location.
- Removing or replacing the broken link if it’s no longer available.
- Monitoring your website regularly so you can quickly identify any problems that arise and address them as soon as possible.
Poorly optimized images
At first glance, image optimization might not seem like a content issue, but having poorly optimized images on your website is definitely something that can reduce page load speed time and consequently prevent users from accessing your content.
Some of the common image optimization issues that lead to slow load times include:
- Images that have the wrong file format.
- Large image files.
- Incorrect image dimensions.
Additionally, images that don’t fit the context of your articles or webpages are oftentimes more distracting than helpful and this ultimately results in a less than ideal user experience.
To identify where your images may be slowing down your site, you can use Google PageSpeed Insights. This tool in particular will provide detailed reports of your image issues, including file sizes, loading times, and potential compression improvements.
Fix poorly optimized images
Where there is a problem, you can find a solution. Here are a few ways to fix your image issues depending on the specific one you may be facing.
- Use image optimization tools, such as Adobe Photoshop or TinyPNG, to optimize your images for the web.
- Use appropriate image formats based on your content. For example, use JPEG for photographs and realistic images and PNG for graphics, logos, and simple illustrations. You can also consider using modern formats like WebP, which you can compress easily without sacrificing the quality.
- Compress your images to reduce the size of the file and ensure you maintain an acceptable image quality.
- Publish images that fit the actual display size on your webpage. Always avoid large images when smaller ones will do.
- Implement lazy loading so that your images only load when they are about to become visible on your user’s screen. Implementing this will significantly help you improve the initial page load times.
- Verify that your images also work well and load quickly for mobile devices.
Wrapping up
The benefits of high-quality content cannot be overstated; it’s something that directly influences how your site appears in the SERPs and has a direct impact on user experience.
When you resolve common SEO content issues, you enhance your overall online presence and the accessibility to your content. As search engines continuously refine their algorithm to satisfy user satisfaction, it’s our job to continuously audit and fix content issues for sustained success.


